Astaxanthin Benefits: The Ultimate Guide to This Super Antioxidant

- Astaxanthin is an organic pigment known as a carotenoid found in microalgae, yeast and marine species.
- As an antioxidant, astaxanthin has several potential benefits. These include improved eye health, reduced signs of aging and increased brain function.
- Astaxanthin-rich foods include lobster, salmon and crawfish. Supplements, such as krill oil, can also help elevate your wellness routine.
Ever wondered what gives some seafood a red hue? Or what makes flamingos’ feathers pink? Enter astaxanthin. It’s a carotene that gives color (pigment) to fish such as salmon, lobster and shrimp.[1] This is not the same as beta-carotene, another pigment from the carotene family. Beta-carotene gives fruits and vegetables like carrots and sweet potatoes their orange coloring.
As a potent antioxidant, astaxanthin has several potential health benefits. These include protection from skin damage due to UV exposure, neuroprotection and reduced biomarkers of inflammation.[2]
Read on to learn what makes this carotene so special, see foods high in astaxanthin and get the scoop on supplements.

What Is Astaxanthin?
Let’s take a deep dive into the definition of astaxanthin.
Astaxanthin is a red carotenoid pigment that provides natural coloring to marine plants and species. Living organisms, such as salmon, lobster, crab and crawfish, don’t produce astaxanthin. Instead, they get this red hue from microalgae and yeast — two food sources that contain astaxanthin.[3]
Some animals develop their pigment through the food chain. For example, the pink coloring of flamingos traces back to their diets, which comprise large amounts of algae and brine shrimp.

Astaxanthin Benefits
You won’t turn fiery red or blush pink from eating too many astaxanthin-rich foods. But you will reap several health benefits, such as:
- High in antioxidants: As one of nature’s most powerful antioxidants, astaxanthin has been hailed as the “king of antioxidants.” This may protect the body from oxidative stress. In simple terms, oxidative stress occurs when there are too many free radicals in the body and not enough antioxidants to neutralize them. Free radicals can come from toxins in the environment, cigarette smoke and ultraviolet light.[4]
- Promotes healthy skin: Vitamins A, C and E get a lot of attention when it comes to healthy, radiant skin. But none of these contain the same sheer antioxidant power of astaxanthin. Studies have found that astaxanthin is 6,000 times more potent than vitamin C and 100 times more potent than vitamin E.[5]
This has fantastic benefits for the skin. A meta-analysis of 11 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies found that astaxanthin may improve wrinkles, increase hydration and protect against UV damage.[6] - Supports brain health:Dealing with oxidative stress over long periods can wreak havoc on the body. For example, it may cause cell damage, premature aging and the development of cancer and diabetes. Oxidative stress can also tamper with a person’s cognitive performance. This is because it can increase the risk of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Astaxanthin acts as antioxidant to reduce oxidative stress and the effects of inflammation in the brain.[7]
Other astaxanthin benefits include:
- Supports heart health
- Supports eye health
- May promote athletic performance
- Immune health support
- Joint comfort and health
Ways to Incorporate Astaxanthin in Your Diet
Adding astaxanthin into your diet through food and supplements is a lot easier — and tastier — than eating the microalgae fish eat.
Astaxanthin in Food
While there are many natural sources of astaxanthin, the most obvious choices are the ones found under the sea. For example, there is about 4.5 mg of astaxanthin in four ounces of salmon.[8]
When it comes to astaxanthin-rich foods, the redder the better. Here are the best astaxanthin-rich foods to add to your diet:
- Sockeye salmon
- Crawfish
- Krill
- Lobster
- Shrimp
- Crab
- Crawfish
- Krill
- Algae
- Trout
Astaxanthin in Supplements
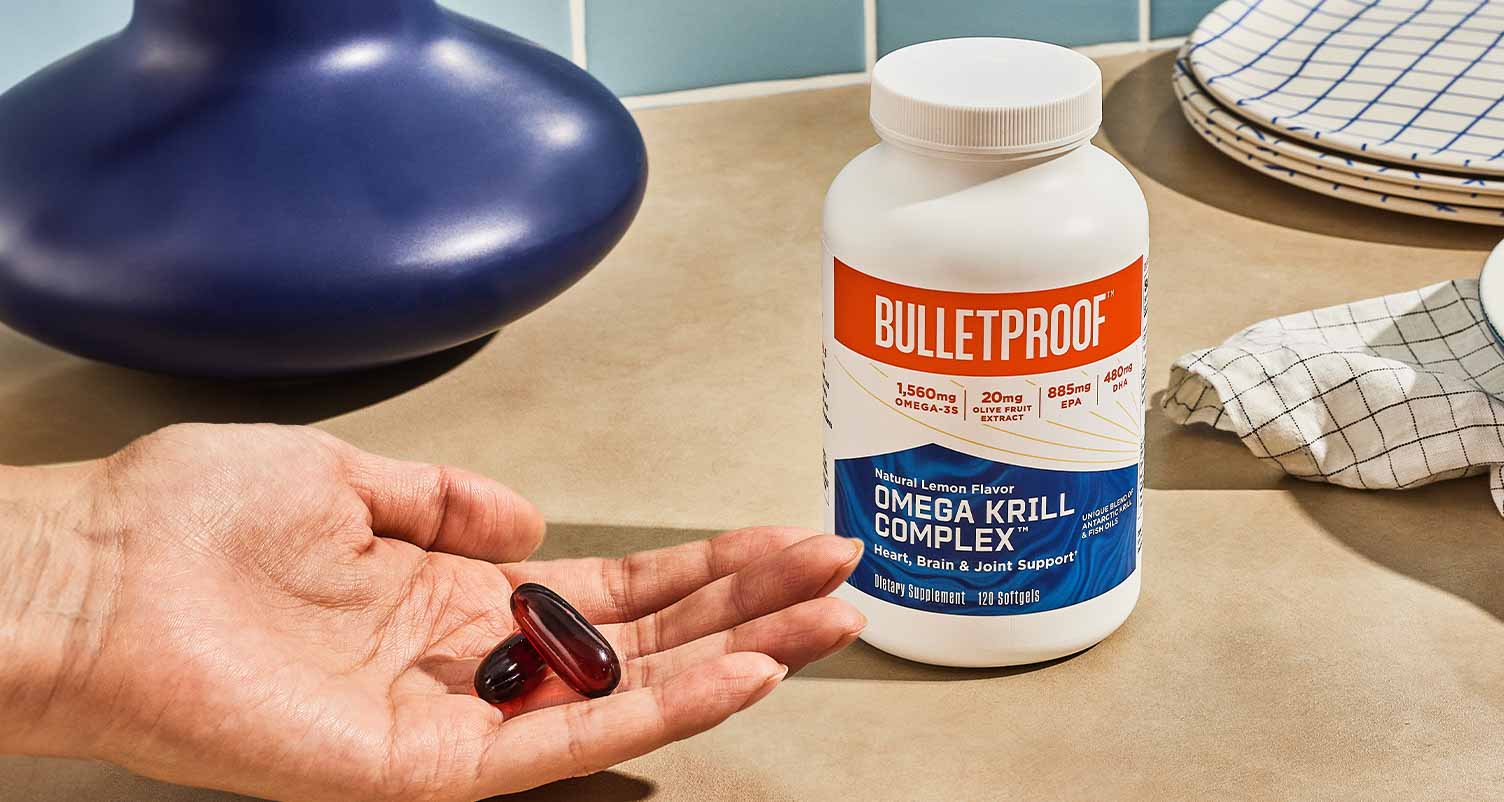
If you’re not a fan of seafood, no worries. Astaxanthin supplements can help. Many supplements extract astaxanthin from a particular type of microalgae. This microalgae is known as Haematococcus pluvialis. Krill oil, a type of supplement that provides omega-3 fatty acids ALA, EPA and DHA, is another source of astaxanthin.
Bulletproof’s Omega Krill Complex is a standout option that has 2 mg of astaxanthin in each capsule to support the heart, skin, eyes and brain. And since each capsule is lemon-flavored, you get all the benefits you love minus the fishy taste.
At this point, you might be wondering, “how much astaxanthin should I take?” While there are no recommended guidelines, research has found that a safe dosage is between 2 and 24 mg per day.[9]
Astaxanthin is a carotene that gives fish and other organisms their red color. But astaxanthin does more than impart color onto seafood and other living organisms. It’s also one of nature’s most powerful sources of antioxidants that has a whole slew of impressive health benefits. This includes improved brain health, skin and prevention of free radicals. It even surpasses other carotenoids for its ability to protect the body from oxidative stress.
Seafood is a great and delicious way to increase astaxanthin in your diet. But, eating too much fish could increase your risk of mercury poisoning.[10] Astaxanthin supplements can help safely fill the nutritional gap.
Sign up for early access to sales, product launches, the latest Bulletproof news and more!



